Difference between revisions of "Python:DAQ 2"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Graph from basic_aio == | == Graph from basic_aio == | ||
Graph showing output when | Graph showing output when | ||
| − | <syntaxhighlight | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> |
v_out = 2.5+2.5*npsin(2*np.pi*k/100); | v_out = 2.5+2.5*npsin(2*np.pi*k/100); | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Circuit2PlotPY.png|500px]] |
</center> | </center> | ||
Revision as of 03:54, 13 November 2018
This page contains pictures and graphs related to DAQ 2 for EGR 103. It has been updated for Fall 2018 and Python.
Contents
Notes
- As before, if the system seems to not recognize Dev1, try Dev2 instead.
Pauses
There are intput commands in the code which will cause the program to wait for an input - specifically when the program first runs to check the lights. You will need to hit return to un-pause the program. The way to see if the program is paused is to look in the console to see if it is waiting for an input.
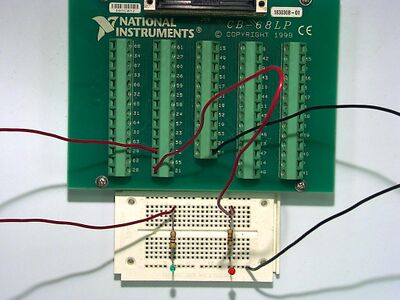
Circuit for basic_aoutput
Circuit layout for BasicAOutput - You only need the left-most circuit, however
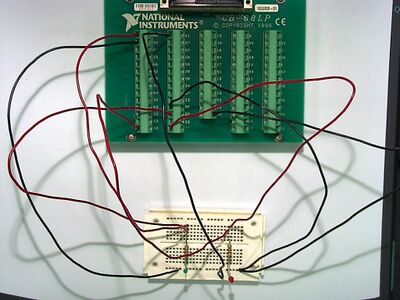
Circuit for basic_aio
Circuit layout for BasicAIO - You only need the left-most circuit, however
Graph from basic_aio
Graph showing output when
v_out = 2.5+2.5*npsin(2*np.pi*k/100);
That is,
\( \begin{align} V_{out}=2.5+2.5\sin\left(\frac{2\pi k}{100}\right) \end{align} \)
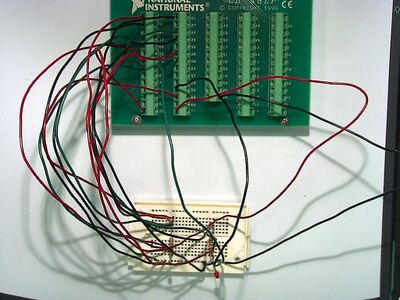
Circuit for aio
Circuit layout for aio - You only need the left-most circuit, however
Graph from aio
Graph showing outputs from three measurement channels. Note at the far left that they all start at either exactly -1 V or 0 V!
Codes
Here are the codes references in the assignment.
basic_aoutput.py
1 #%% Import modules
2 import numpy as np
3 import time
4 import PyDAQmx as daq
5
6
7
8 #%% Create a task
9 taskout = daq.Task()
10
11
12 #%% Set Channel Counts
13 a_out = 1
14
15
16 #%% Add analog output lines
17 taskout.CreateAOVoltageChan('Dev1/ao0:{}'.format(a_out-1),'',
18 -10.0,10.0,daq.DAQmx_Val_Volts,None)
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 #%% Define useful functions
26 # Function to change daq outputs
27 def write_volts(data):
28 taskout.WriteAnalogScalarF64(1,10.0,data,None)
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39 #%% Stop and start tasks
40 taskout.StopTask()
41 taskout.StartTask()
42
43
44
45 #%% Check lights
46 write_volts(5)
47 input('PAUSED - Hit return to continue ')
48 print('Running')
49 write_volts(0)
50
51 #%% Write values to output
52
53 for k in range(300):
54 v_out = 2.5+2.5*np.sin(2*np.pi*k/100)
55 write_volts(v_out)
56 time.sleep(0.01)
57
58
59 #%% Turn all off when finished and stop task
60 write_volts(0)
61 taskout.StopTask()
basic_aio.py
1 #%% Import modules
2 import numpy as np
3 import time
4 import PyDAQmx as daq
5 import ctypes
6 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7
8 #%% Create a task
9 taskout = daq.Task()
10 taskin = daq.Task()
11
12 #%% Set Channel Counts
13 a_out = 1
14 a_in = 1
15
16 #%% Add analog output lines
17 taskout.CreateAOVoltageChan('Dev1/ao0:{}'.format(a_out-1),'',
18 -10.0,10.0,daq.DAQmx_Val_Volts,None)
19
20 #%% Add analog input lines
21 taskin.CreateAIVoltageChan('Dev1/ai0:{}'.format(a_in-1),'',
22 daq.DAQmx_Val_Cfg_Default,
23 -10.0,10.0,daq.DAQmx_Val_Volts,None)
24
25 #%% Define useful functions
26 # Function to change daq outputs
27 def write_volts(data):
28 taskout.WriteAnalogScalarF64(1,10.0,data,None)
29
30 # Function to read daq outputs
31 def read_volts():
32 data = np.zeros((1,a_in), dtype=np.float64)
33 read = ctypes.c_int32()
34 taskin.ReadAnalogF64(1,10.0,
35 daq.DAQmx_Val_GroupByChannel,
36 data, a_in, ctypes.byref(read), None)
37 return data
38
39 #%% Stop and start tasks
40 taskout.StopTask()
41 taskin.StopTask()
42 taskout.StartTask()
43 taskin.StartTask()
44
45 #%% Check lights
46 write_volts(5)
47 input('PAUSED - Hit return to continue ')
48 print('Running')
49 write_volts(0)
50
51 #%% Write and read values
52 meas = np.zeros((300,3), dtype=np.float64)
53 for k in range(300):
54 v_out = 2.5+2.5*np.sin(2*np.pi*k/100)
55 write_volts(v_out)
56 time.sleep(0.01)
57 meas[k,:] = read_volts()
58
59 #%% Turn all off when finished and stop task
60 write_volts(0)
61 taskout.StopTask()
62 taskin.StopTask()
63
64 #%% Make plots
65 plt.figure(1)
66 plt.clf()
67 total = meas[:,0]
68
69
70 plt.plot(total, 'b')
aio script
1 #%% Import modules
2 import numpy as np
3 import time
4 import PyDAQmx as daq
5 import ctypes
6 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7
8 #%% Create a task
9 taskout = daq.Task()
10 taskin = daq.Task()
11
12 #%% Set Channel Counts
13 a_in = 3
14 a_out = 1
15
16 #%% Add analog output lines
17 taskout.CreateAOVoltageChan('Dev1/ao0:{}'.format(a_out-1),'',
18 -10.0,10.0,daq.DAQmx_Val_Volts,None)
19
20 #%% Add analog input lines
21 taskin.CreateAIVoltageChan('Dev1/ai0:{}'.format(a_in-1),'',
22 daq.DAQmx_Val_Cfg_Default,
23 -10.0,10.0,daq.DAQmx_Val_Volts,None)
24
25 #%% Define useful functions
26 # Function to change daq outputs
27 def write_volts(data):
28 taskout.WriteAnalogScalarF64(1,10.0,data,None)
29
30 # Function to read daq outputs
31 def read_volts():
32 data = np.zeros((1,a_in), dtype=np.float64)
33 read = ctypes.c_int32()
34 taskin.ReadAnalogF64(1,10.0,
35 daq.DAQmx_Val_GroupByChannel,
36 data, a_in, ctypes.byref(read), None)
37 return data
38
39 #%% Stop and start task
40 taskout.StopTask()
41 taskin.StopTask()
42 taskout.StartTask()
43 taskin.StartTask()
44
45 #%% Check lights
46 write_volts(5)
47 input('PAUSED - Hit return to continue ')
48 print('Running')
49 write_volts(0)
50
51 #%% Write and read values
52 meas = np.zeros((300,3), dtype=np.float64)
53 for k in range(300):
54 v_out = (k/299)*10
55 write_volts(v_out)
56 time.sleep(0.01)
57 meas[k,:] = read_volts()
58
59 #%% Turn all off when finished and stop task
60 write_volts(0)
61 taskout.StopTask()
62 taskin.StopTask()
63
64 #%% Make plots
65 plt.figure(1)
66 plt.clf()
67 total = meas[:,0]
68 resv = meas[:,1]
69 ledv = meas[:,2]
70 plt.plot(total, 'b', resv, 'g', ledv, 'r')
71 plt.legend(['$v_s$', '$v_R$', '$v_{LED}$'])
72
73 #%% Save values and figure
74 color = input('Color: ')
75 eval("plt.title('{:s}')".format(color))
76 fid=eval("open('{:s}_data.dat', 'w')".format(color))
77 for k in range(300):
78 fid.write('{:.4e} {:.4e} {:.4e}\n'.format(*meas[k,:]))
79 fid.close()
80 eval("plt.savefig('{:s}_plot.png')".format(color))
Questions
Post your questions by editing the discussion page of this article. Edit the page, then scroll to the bottom and add a question by putting in the characters *{{Q}}, followed by your question and finally your signature (with four tildes, i.e. ~~~~). Using the {{Q}} will automatically put the page in the category of pages with questions - other editors hoping to help out can then go to that category page to see where the questions are. See the page for Template:Q for details and examples.